

In 1940–41 another advance in the reactive propulsion field took place: the development and serial production of the Katyusha multiple rocket launcher.ĭuring the 1930s Soviet rocket technology was comparable to Germany's, but Joseph Stalin's Great Purge severely damaged its progress. On August 18, 1933, GIRD launched the first Soviet liquid-fueled rocket Gird-09, and on November 25, 1933, the first hybrid-fueled rocket GIRD-X.

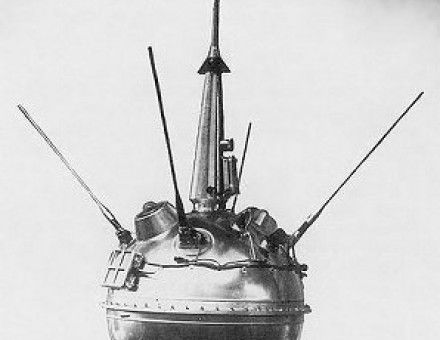
Practical aspects built on early experiments carried out by members of the reactive propulsion study group, GIRD (founded in 1931) in the 1920s and 1930s, where such pioneers as Ukrainian engineer Sergey Korolev-who dreamed of traveling to Mars : 5 -and the Baltic German engineer Friedrich Zander worked. The theory of space exploration had a solid basis in the Russian Empire before the First World War with the writings of Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (1857–1935), who published pioneering papers in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and in 1929 introduced the concept of the multistaged rocket. Kazakhstan created KazCosmos in the 21st century, Russia created an aerospace agency called Rosaviakosmos, which is now a space agency called Roscosmos, and Ukraine created the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). With the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Ukraine inherited the program. Setbacks included the deaths of Korolev, Vladimir Komarov (in the Soyuz 1 crash), and the Soyuz 11 crew between 19, and failure to develop the N-1 super heavy-lift rocket (1968–1974) intended to launch crewed lunar landings. Ultimately, as a result of Mikhail Gorbachev's policy of glasnost in the 1980s, many facts about the space program were declassified. īecause of the program's classified status, and for propaganda value, announcements of the outcomes of missions were delayed until success was certain, and failures were kept secret unless detected by Western tracking stations. Unlike its American competitor, which had NASA as a single coordinating agency, the Soviet space program was split among several competing design bureaus led by Sergei Korolev, Kerim Kerimov, Mikhail Yangel, Valentin Glushko, Vladimir Chelomey, Viktor Makeyev, Mikhail Reshetnev, etc. Sergei Korolev was the head of the principal design group his official title was Chief Designer (a standard title for similar positions in the Soviet Union). The rocket and space program of the Soviet Union, which initially employed captured scientists from the V-2 rocket program, was performed mainly by Soviet engineers and scientists after 1955, and was based on some unique Soviet and Imperial Russian theoretical developments, many derived by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, sometimes known as the father of theoretical astronautics. They also launched some of the first interplanetary probes: Venera 1 and Mars 1 to fly by Venus and Mars, respectively, Venera 3 and Mars 2 to impact the respective planet surface, and Venera 7 and Mars 3 to make soft landings on these planets. They later established the first space station ( Salyut 1), and built the Mir space station, The Soviets were also the first to achieve a few lunar exploration milestones: First Moon impact ( Luna 2), first image of the far side of the Moon ( Luna 3) and uncrewed lunar soft landing ( Luna 9), first space rover ( Lunokhod 1), and first sample of lunar soil automatically extracted and brought to Earth ( Luna 16). It also placed the first woman in Earth orbit ( Valentina Tereshkova on Vostok 6), and a cosmonaut performed the first spacewalk ( Alexei Leonov on Voskhod 2). Over its 38-year history, the Soviet space program developed the first intercontinental ballistic missile ( R-7), launched the first satellite ( Sputnik 1), put the first animal in Earth orbit (the dog Laika on Sputnik 2), and placed the first human in space and Earth orbit ( Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1). The Soviet Union developed expendable launch vehicles, launched artificial satellites, starting in 1953, and had a human spaceflight program.
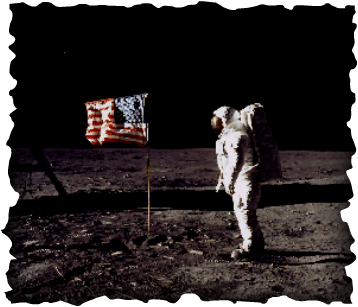
The recruitment of thousands of German specialists in the Operation Osoaviakhim became "an essential catalyst" for the space program. The Soviet space program ( Russian: Космическая программа СССР, romanized: Kosmicheskaya programma SSSR) was the national space program of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), conducted in competition with its Cold War adversary the United States, known as the Space Race from the mid-1950s until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
